The field of neurology has long grappled with the challenges of accurately assessing cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) dynamics, a critical component in diagnosing and managing various neurological disorders. Traditional methods, while useful, often fall short in providing real-time, high-resolution data. However, recent breakthroughs in imaging and sensor technologies are ushering in a new era of precision medicine, enabling clinicians to monitor CSF flow with unprecedented clarity and detail.
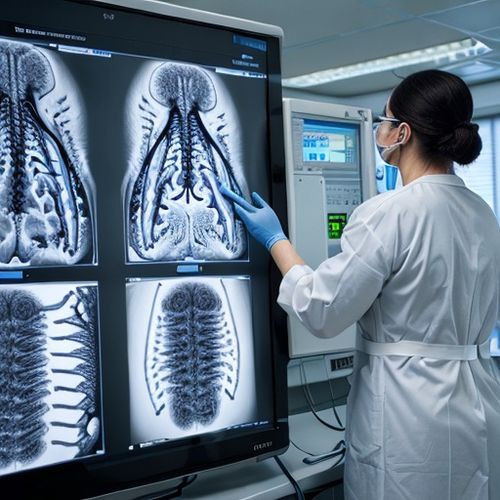
One of the most promising developments is the integration of advanced MRI techniques with computational fluid dynamics. Unlike conventional imaging, these new protocols capture the subtle pulsations and directional flow of CSF within the ventricular system and spinal canal. Researchers at several leading institutions have demonstrated that this approach can detect abnormalities in flow patterns associated with conditions like hydrocephalus, Chiari malformations, and even early-stage neurodegenerative diseases. The implications for early intervention and personalized treatment plans are profound.
Beyond imaging, miniaturized wireless sensors are making waves in both clinical and research settings. These implantable devices, some no larger than a grain of rice, continuously monitor pressure gradients and flow rates without restricting patient mobility. Early trials show they can provide weeks of uninterrupted data, revealing circadian variations in CSF dynamics that were previously impossible to track. This technology is particularly transformative for patients requiring long-term monitoring, as it eliminates the need for repeated invasive procedures.
The marriage of artificial intelligence with CSF analysis represents another leap forward. Machine learning algorithms trained on vast datasets can now identify subtle flow anomalies that might escape human detection. At Massachusetts General Hospital, a deep learning system recently achieved 94% accuracy in predicting shunt failure in hydrocephalus patients by analyzing minute changes in flow characteristics. Such predictive capabilities could significantly reduce emergency hospitalizations and improve quality of life for chronic patients.
Challenges remain in standardizing these technologies across healthcare systems. The high cost of advanced MRI protocols currently limits their widespread adoption, while regulatory hurdles slow the approval of implantable sensors. Nevertheless, the pace of innovation suggests these barriers will likely diminish within the coming decade. Several biotech startups are already developing more affordable, portable monitoring solutions that could bring advanced CSF analysis to community hospitals.
Perhaps most exciting is the potential for these technologies to unravel longstanding mysteries about CSF's role in brain health. Emerging research indicates that impaired CSF flow may contribute to the accumulation of toxic proteins in Alzheimer's disease and other dementias. The ability to precisely map these flow disturbances opens new avenues for both diagnosis and therapeutic development. Some experimental treatments already in trials aim to enhance CSF circulation as a means of clearing pathological proteins from the brain.
As these technologies mature, they promise to transform our understanding of not just pathological conditions, but normal brain physiology as well. The next five years will likely see the first widespread clinical applications of next-generation CSF monitoring, marking a significant milestone in neurological care. For patients suffering from conditions once considered diagnostically challenging, these advances can't come soon enough.

By Thomas Roberts/Apr 19, 2025

By Michael Brown/Apr 19, 2025
By Victoria Gonzalez/Apr 19, 2025
By Benjamin Evans/Apr 19, 2025

By Eric Ward/Apr 19, 2025

By Emily Johnson/Apr 19, 2025

By David Anderson/Apr 19, 2025

By Olivia Reed/Apr 19, 2025

By Emma Thompson/Apr 19, 2025

By William Miller/Apr 19, 2025
By Laura Wilson/Apr 19, 2025

By Emma Thompson/Apr 19, 2025

By John Smith/Apr 19, 2025
By John Smith/Apr 19, 2025
By James Moore/Apr 19, 2025

By Michael Brown/Apr 19, 2025
By John Smith/Apr 19, 2025

By Noah Bell/Apr 19, 2025
By Emma Thompson/Apr 19, 2025

By Benjamin Evans/Apr 19, 2025